Hair Loss Glossary
Alopecia
Hair loss or baldness caused by hereditary disposition, illness, or any functional disorder is called alopecia in medical terms.
Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune disease in which loss of hair occurs in some or all areas of the body is called alopecia areata. Since it causes bald spots on the scalp, it is also known as spot baldness.
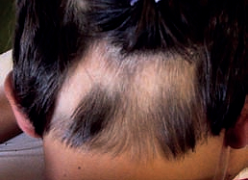
Alopecia Totalis
Loss of complete hair on the scalp is known as alopecia areata. It is an advanced form of alopecia areata.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common form of hair loss in both men and women. In men, this condition is called as male-pattern baldness. Hair fall in a well-defined pattern from above both temples, eventually receding to form a characteristic “M” shape.
The pattern of hair loss in women is different from that of men. In women, hair become thinner all over the head. Hairline does not recede.
Alopecia Universalis
The complete loss of hair from the scalp and body is called alopecia universalis. It is an autoimmune condition in which a person’s own immune system attacks hair follicles. An itching and burning sensation are two common signs of alopecia universalis.
Anagen
The growing phase of hair growth cycle is called anagen. The duration of this phase usually lasts between one and seven years.
Anagen Effluvium
Loss of hair that are in the growing or anagen phase of hair growth cycle is called anagen effluvium. This is usually caused by chemotherapy or radiation treatment.
Androgen
It is a male hormone. Testosterone is the major androgen.
Catagen
The second phase of the hair growth cycle is called as catagen phase. It comes after anagen phase.
Crown Area
The area on the top back of the head that has a swirl or spiral pattern of hair is called crown area. It is also known as the “Vertex”. Usually, the first sign of hair loss is seen here.
Cuticle
The outer layer of a hair is called cuticle. It is the hair’s protective shield.
Dermal Papilla
A structural formation at the base of hair follicles is called dermal papilla. It provides oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles ensuring their healthy growth.
Dermis
The second layer of the skin is called as the dermis. It is the innermost layer.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
It is a male hormone responsible for hair loss. DHT is created after male hormone testosterone comes in contact with the enzyme 5-alpha reductase.
Direct Hair Transplantation (DHI) Technique
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) is the most advanced hair transplant technique in which hair follicles are implanted one by one directly on the affected area of the scalp. Each and every hair follicle is placed by a DHI surgeon using unique single-use instruments that provide full control over direction, angle, and depth. DHI ensures 100% natural results as well as the maximum survival rate of follicles.
The hair transplanted by DHI DirectTM technique do not fall out. They grow naturally through one’s lifetime.
Donor Site
The lower back of the head where the density of hair usually remains thick for a lifetime is called donor area.
Donor Hair
Hair in the donor area are called donor hair. They are extracted and implanted to cover scalp area suffering from hair loss.
Epidermis
The outer layer of the skin is called epidermis. It is nonvascular.
5-Alpha Reductase
It is a type of a chemical. It transforms testosterone into dihydrotestosterone.
5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors
It blocks the action of the enzymes 5-alpha reductase and prevents the body from converting testosterone into DHT.
Female Pattern Baldness
A hereditary pattern of hair loss in women is known as female pattern baldness. Female pattern baldness is different from male pattern baldness. In this condition, women generally experience thinning of hair all over the head. Women do not experience receding hairline.
Finasteride
Manufactured by Merck, the drug Proscar is also called Finasteride and Propecia. It is believed to be effective in treatment for hair loss.
Follicle
It is the root of hair below the surface of the scalp. It looks like a bulb and sack sometimes. It is a sheath in which hair grows.
Follicular Unit
A group of one or more hair follicles is called a follicular unit. A follicular unit generally has 2.4 hairs.
Frontal Alopecia
Frontal Alopecia is characterized by the loss of hair at the front of the head.
Genetic
Belonging or relating to genes received by each human, animal, and plant from its parents.
Grafting
A procedure in which skin containing hair follicles is removed from the donor area and implanted in the recipient area. Minigrafting (3-8 hairs) and micrografting (1-2 hairs) are two popular methods of grafting.
Grafts
Transplanted hair.
Hair Follicle
A strand of hair with its root is called a hair follicle. They are extracted from the donor area and implanted on the recipient area.
Hair Plugs
It is a slang term for the large round grafts. They are not used much nowadays.
Hair Transplant
A surgical procedure in which hair follicles are transferred from the lower back of the head to the recipient area by the surgeon.
Hair Weaving
A process in which a hair piece is attached to existing hair on the scalp.
Hamilton Scale
A method proposed by Hamilton to rate the extent of hair loss.
Keratin
It is a type of insoluble, tough, and fibrous protein which forms hair and skin.
Male Pattern Baldness
One of the most common forms of hair loss in men, male-pattern baldness affects more than 50% men over the age of 50. Hairs fall in a well-defined pattern from above both temples, eventually receding to form a characteristic “M” shape.
Melanin
Pigmenting granules present in keratin fibre of the hair shaft. It determines the colour of the hair. It reduces with age resulting in gray or white hair.
Minigraft
A small hair graft which contains three to eight hair follicles.
Non-Scarring Alopecia
Loss of hair without any scarring is called as non-scarring alopecia. It is also known as noncicatricial alopecia.
Norwood Scale
A scale to measure the extent of hair loss is called Norwood scale.
Recipient Site
The area affected by hair loss or the area where donor hairs are transplanted is called recipient area.
Scalp Reduction
A surgical treatment to remove scalp areas affected by alopecia. The main purpose is to reduce the overall bald area from the scalp.
Suture
Stitch
Telogen
The resting phase of hair growth cycle is called telogen. It lasts for 3 months.
Telogen Effluvium
This is the second most common form of hair loss after androgenic alopecia. This condition causes hairs enter into the telogen phase.
Telogen Loss
Loss of hair in the telogen phase is called telogen loss. It is also called the natural loss of hair.
Testosterone
Male hormones responsible for the development of male characteristics.
Traction Alopecia
As the name suggests, this type of hair loss is caused by the traction applied to hair. It is commonly associated with braiding, ponytails, and other types of hairstyles that put pressure on hair.
Trichotillomania
Hair loss caused by constant pulling and twirling is called trichotillomania.
Vertex
The crown area of the scalp is also called as a vertex.